"Applications of Electromagnets" Magical electromagnet PPT courseware Simple campus recruitment activity planning plan summary enterprise and institution recruitment publicity lecture PPT template is a general PPT template for business post competition provided by the manuscript PPT, simple campus recruitment activity planning plan summary enterprise and institution recruitment promotion Lecture PPT template, you can edit and modify the text and pictures in the source file by downloading the source file. If you want more exquisite business PPT templates, you can come to grid resource. Doug resource PPT, massive PPT template slide material download, we only make high-quality PPT templates!
| 文件名 如何下载使用 | 下载次数 | Download Points | 下载地址 |
|---|---|---|---|
| "Applications of Electro... | 8450次 | 0.00 | Free Download |
Tips: If you open the template and feel that it is not suitable for all your needs, you can search for related content "Applications of Electromagnets" Magical electromagnet PPT courseware is enough.
How to use the Windows system template
Directly decompress the file and use it with office or wps
How to use the Mac system template
Directly decompress the file and use it Office or wps can be used
Related reading
For more detailed PPT-related tutorials and font tutorials, you can view: Click to see
How to create a high-quality technological sense PPT? 4 ways to share the bottom of the box
Notice
Do not download in WeChat, Zhihu, QQ, built-in browsers, please use mobile browsers to download! If you are a mobile phone user, please download it on your computer!
1. The manuscript PPT is only for study and reference, please delete it 24 hours after downloading.
2. If the resource involves your legitimate rights and interests, delete it immediately.
3. Contact information: service@daogebangong.com
"Applications of Electromagnets" Magical electromagnet PPT courseware, due to usage restrictions, it is only for personal study and reference use. For commercial use, please go to the relevant official website for authorization.
(Personal non-commercial use refers to the use of this font to complete the display of personal works, including but not limited to the design of personal papers, resumes, etc.)

Related reading
For more detailed PPT-related tutorials and font tutorials, you can view:Please click to see








Authoritative PPT Summary
"Applications of Electromagnets" Magical electromagnet PPT courseware
consolidate
1. Mark the N and S poles of the energized solenoid in the picture on the right, and mark the positive and negative poles of the power supply.
2. To make the magnetic poles of the electromagnet look like the picture on the right, please connect the two endpoints a and b of the wire to the two poles of the power supply.
discuss
1. How does an electromagnet work?
2. What is the difference between electromagnets and ordinary magnets?
3. How can the presence and strength of the magnetism of the electromagnet be controlled?
4. Why is the core of electromagnet made of soft iron? And not made of steel?
5. Why is the magnetism greatly enhanced after inserting the iron core?
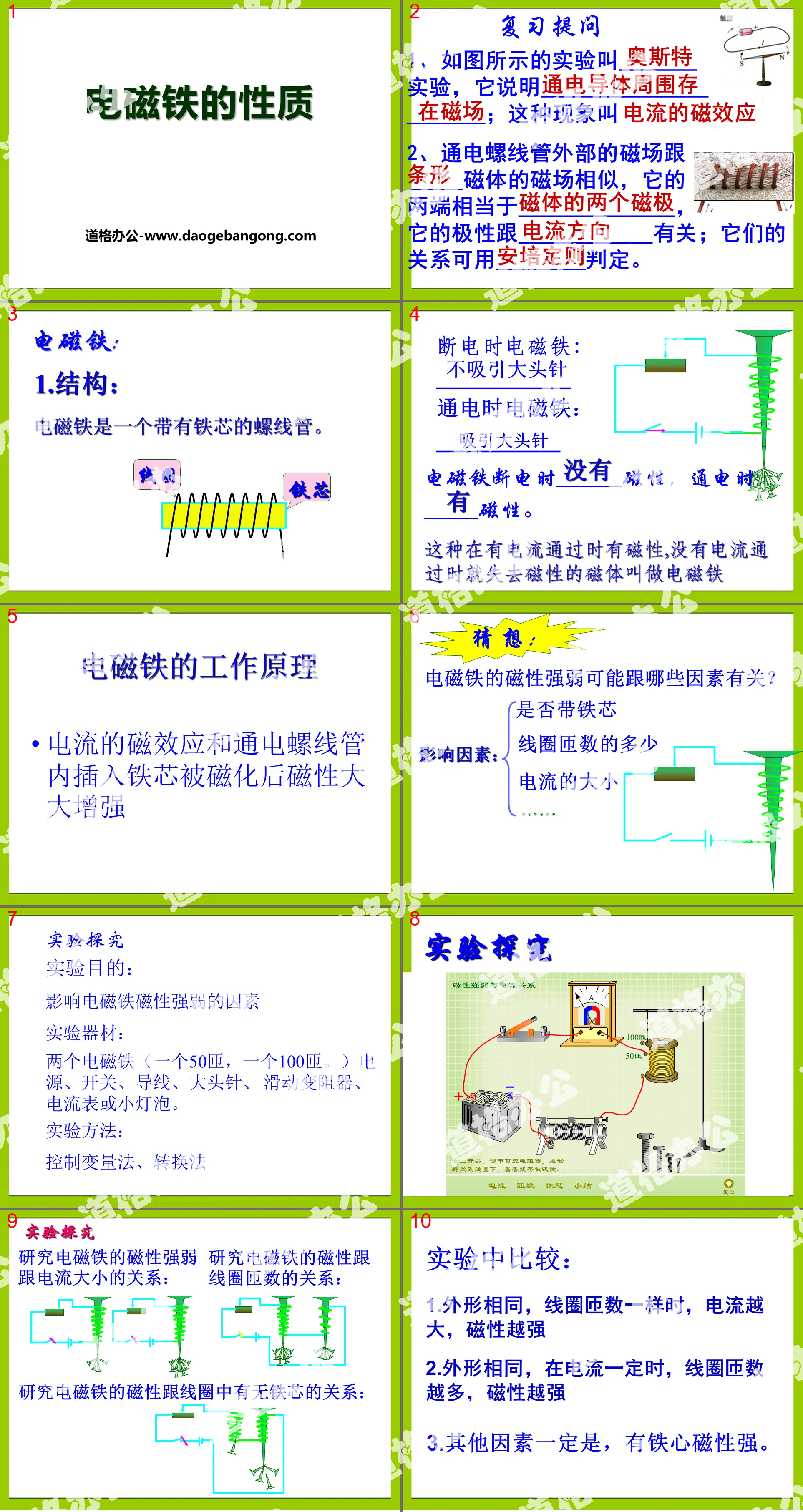
Electromagnet: An energized solenoid with an iron core.
advantage:
1. The presence or absence of magnetism can be controlled, that is, the electromagnet is non-magnetic when the current is turned off.
2. The strength of magnetism can be controlled, that is, when the current is large, the magnetism is strong.
3. The direction of the magnetic field can be controlled, that is, when the direction of the current changes, the direction of the magnetic field changes.
Working principle: Close the switch, current passes through the electromagnet, and the magnet generates magnetism to attract the elastic piece, causing the hammer to hit the iron bell to make a sound. At the same time, the circuit is disconnected, the electromagnet loses its magnetism, and the circuit is closed again due to the elasticity of the elastic piece. . The above process is repeated in cycles, and the electric bell continues to make sounds.
Electromagnetic relay
1. Definition: An electromagnetic relay is an automatic switch controlled by an electromagnet.
2. Structure of electromagnetic relay
It consists of electromagnet, armature, spring and contacts. Its working circuit consists of two parts: a low-voltage control circuit and a high-voltage working circuit.
3. Features:
Use low voltage and weak current to control high voltage and strong current
The control function of electromagnetic relay
When the switch K is closed, the electromagnetic relay starts to work. The electromagnet pulls the armature down, turns on the high-voltage working circuit, the motor starts to work, and the light bulb L goes out. When the switch K is turned off, the electromagnet loses its magnetism, and the spring pulls the armature down, and the working circuit disconnect
4. Working principle: Close the switch K, connect the low-voltage circuit, the electromagnet generates magnetism, attract the armature, connect the high-voltage working circuit, the green light turns on, the motor starts to work, and the red light goes out. When switch K is turned off, the electromagnetic relay stops working and the red light shines.
The control circuit switch is used to control the presence or absence of magnetism of the electromagnet, and the armature is sucked and released to drive the contacts to control the working circuit.
Electromagnetic relay acts as a switch
How does the maglev train work?
Maglev trains are high-tech vehicles that utilize the attraction and repulsion of magnetic poles. The repulsive force makes the train hang, and the attractive force makes the train move. Maglev train carriages are equipped with superconducting magnets and coils are installed at the bottom of the railway. After being powered on, the polarity of the magnetic field generated by the ground coil always remains the same as the polarity of the electromagnet in the carriage. The two "magnetic poles with the same name repel each other", and the repulsive force makes the train levitate.
Unlike conventional trains, which are powered by a locomotive, maglev trains are powered by the track. Electromagnets are installed on the sides of the track, which interact with the magnets on the train.
When the train is running, the magnet (N pole) at the front of the car is attracted by the electromagnet (S pole) farther forward on the track, and at the same time repelled by the electromagnet (N pole) farther back on the track - the result is that the front " Pull" and "push" behind to make the train move forward.
Keywords: electromagnet application teaching courseware, magical electromagnet teaching courseware, People's Education Edition fourth grade science PPT courseware download, fourth grade science slide courseware download, electromagnet application PPT courseware download, magical electromagnet PPT Courseware download, .PPT format;
For more information about the PPT courseware "Applications of Electromagnets and Magical Electromagnets", please click on the Applications of Electromagnets ppt Magical Electromagnets ppt tag.
"Applications of Electromagnets" PPT:
"Applications of Electromagnets" PPT Part One: Electromagnets Electromagnets: energized solenoid with an iron core inside. The working principle of electromagnet: It works by using the magnetic effect of electric current. 1. The electromagnet is a _________ with ________. 2. The electromagnet...
"Applications of Electromagnets" Magical Electromagnet PPT Courseware 3:
"Applications of Electromagnets" Magical Electromagnet PPT Courseware 3 1. What is an electromagnet? 1. Definition: An electromagnet is an energized solenoid with an iron core. 2. Structure: Coil Iron core 2. Electromagnet: 1. Design a simple electromagnet and think about the following questions..
"Applications of Electromagnets" Magical Electromagnet PPT Courseware 2:
"Applications of Electromagnets" Magical Electromagnet PPT Courseware 2 Creation Scenario Electromagnets are widely used in production and life: such as: electromagnetic lifting, electromagnetic concentrators, telephones, electric bells, electromagnetic relays, etc. Knowledge point 1: Electromagnetic relay Electromagnetic relay 1. Structure:..