People's Education Press High School Chemistry Compulsory Course I
Cantonese Education Edition Ninth Grade Chemistry Volume 1
Beijing Curriculum Reform Edition Ninth Grade Chemistry Volume 2
People's Education Press Ninth Grade Chemistry Volume 1
Beijing Curriculum Reform Edition Ninth Grade Chemistry Volume 1
Lu Ke Edition High School Chemistry Compulsory Course 1
Lu Jiao Edition Ninth Grade Chemistry Volume 1
People's Education Press Ninth Grade Chemistry Volume 2
Cantonese Education Edition Ninth Grade Chemistry Volume 2
Hunan Education Edition Ninth Grade Chemistry Volume 1
Lu Ke Edition High School Chemistry Compulsory Course 2
People's Education Press High School Chemistry Compulsory Course 2
Hunan Education Edition Ninth Grade Chemistry Volume 2
Lu Jiao Edition Ninth Grade Chemistry Volume 2

| Category | Format | Size |
|---|---|---|
| Lu Ke Edition High School Chemistry Compulsory Course 2 | pptx | 6 MB |
Description
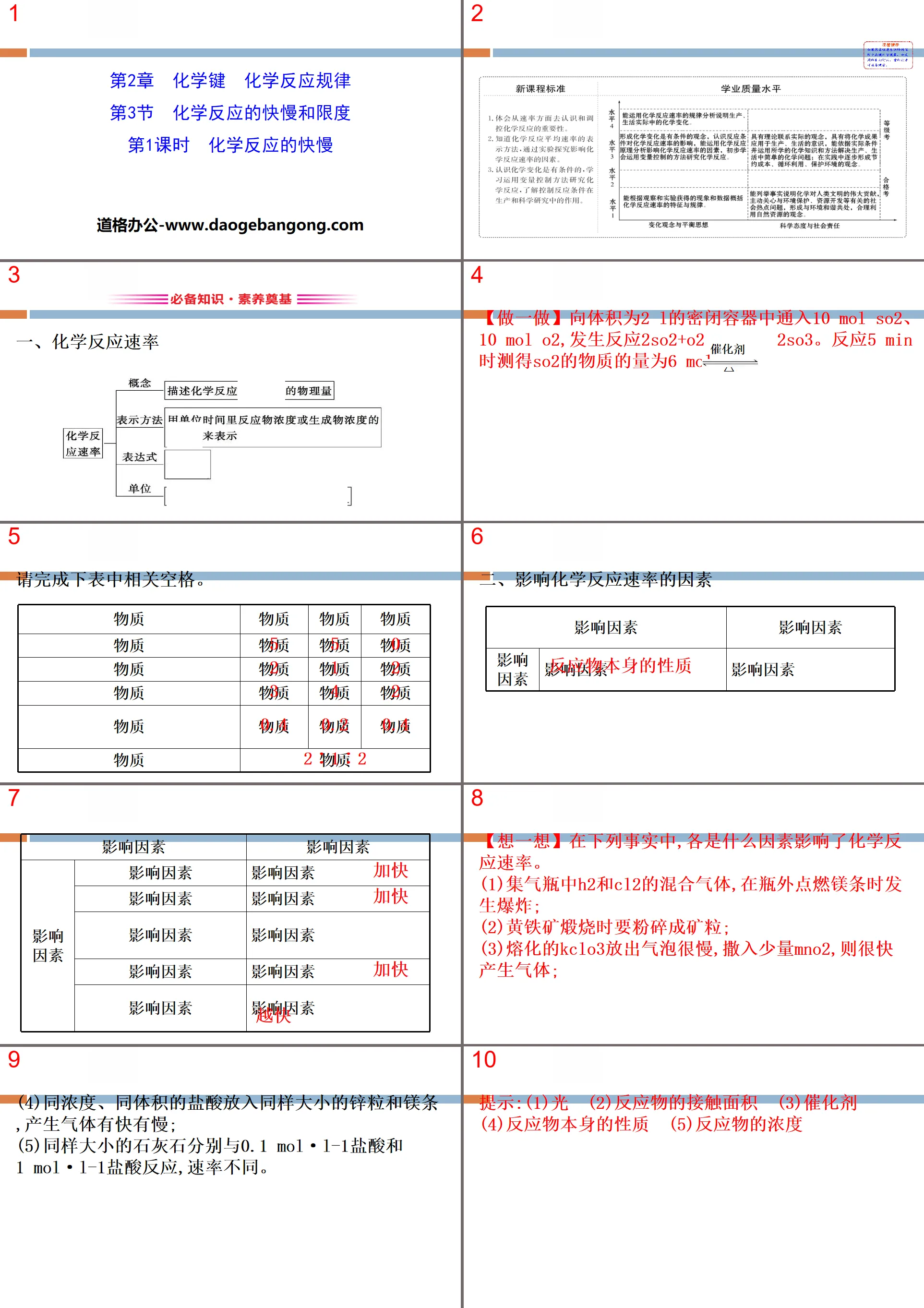
"The Speed and Limits of Chemical Reactions" Chemical Bonding and Chemical Reaction Rules PPT (Lesson 1: The Speed of Chemical Reactions)
Part 1: Essential knowledge and foundation of literacy
1. Chemical reaction rate
[Do it] Pour 10 mol SO2 and 10 mol O2 into a closed container with a volume of 2 L, and the reaction 2SO2+O2 == 2SO3 will occur. The amount of SO2 measured during the reaction for 5 minutes was 6 mol.
2. Factors affecting the rate of chemical reactions
[Think about it] In the following facts, what factors affect the rate of chemical reactions?
(1) The mixed gas of H2 and Cl2 in the gas collection bottle explodes when the magnesium bar is ignited outside the bottle;
(2) When pyrite is calcined, it must be crushed into ore particles;
(3) Melted KClO3 releases bubbles very slowly, and if a small amount of MnO2 is sprinkled, gas will be generated quickly;
(4) When zinc particles and magnesium strips of the same size are put into hydrochloric acid of the same concentration and volume, the gas will be generated quickly or slowly;
(5) Limestone of the same size is mixed with 0.1 mol·L-1 hydrochloric acid and
1 mol·L-1 hydrochloric acid reacts at different rates.
Tips: (1) Light (2) Contact area of reactants (3) Catalyst
(4) The nature of the reactant itself (5) The concentration of the reactant
3. The significance of regulating chemical reaction rates
【Situation·Thinking】
Food additives are synthetic or natural substances added to food to improve the color, aroma, taste and other qualities of food, as well as to meet the needs of preservation and processing technology. For example, lipid antioxidants are a common food additive.
Please analyze how oil antioxidants utilize the principle of chemical reaction rate.
Tip: The purpose of adding antioxidants to food is to slow down the deterioration rate of food, which is related to the reaction rate.
PPT on the speed and limits of chemical reactions, part 2: key abilities and literacy formation
Knowledge point 1: Calculation and comparison of chemical reaction rates
[Key points to clarify doubts]
1. Calculation of chemical reaction rates
(1) Definition formula: v(A)=
(2) Relational expression method: for chemical reactions:
aA(g)+bB(g)====cC(g)+dD(g), satisfies the following relationship:
v(A):v(B):v(C):v(D)=a:b:c:d.
The above relationship can be summarized as the ratio of chemical reaction rate values = the ratio of stoichiometric numbers.
2. Comparison of chemical reaction rates
(1) Normalization method: ① Unify units: If the units are not unified, they must be converted into the same units; ② Conversion: If the reaction rates are expressed by different substances, they must be converted into the same substance to express the reaction rates; ③ Comparison: Compare the values. The larger the value, the faster the reaction rate.
[Knowledge Expansion] "Three-stage formula" calculation of chemical reaction rate
(1) Calculation mode
Let a mol·L-1 and b mol·L-1 be the initial concentrations of the two substances A and B respectively, mx mol·L-1 be the conversion concentration of reactant A, nx mol·L-1 be the Conversion concentration, then:
(2)Basic steps
① Determine the starting amount of reactants or products;
② Determine the amount of change of each substance during the reaction;
③ Determine the amount of each substance when the reaction proceeds to a certain moment;
④ Establish an equation relationship based on the conditions in the question stem to answer;
⑤ Apply the proportional relationship to answer: the ratio of chemical reaction rates = the ratio of concentration changes = the ratio of changes in the amount of substances = the ratio of stoichiometric numbers.
【Think·Discussion】
(1) If mol·L-1·min-1 is used as the unit of chemical reaction rate, can a solid be used to express the reaction rate of a certain reaction?
Tip: No. The concentration of solid or pure liquid is regarded as a constant, Δc=0, so solid or pure liquid is not used to express the chemical reaction rate.
(2) Is the reaction rate the instantaneous rate of the chemical reaction at a certain moment?
Hint: No. The chemical reaction rate is the average reaction rate over a period of time, not the instantaneous rate at a certain moment.
Knowledge point 2: The influence of external conditions on the rate of chemical reactions
[Key points to clarify doubts]
1.Concentration
(1) Only applicable to chemical reactions in which gas participates or occurs in solution.
(2) At a certain temperature, the concentration of solid or pure liquid substances is a constant, and changing its dosage has no effect on the rate of chemical reaction.
2.Temperature
(1) It is applicable to any chemical reaction and is not affected by the state of the reactants.
(2) Whether it is an endothermic reaction or an exothermic reaction, increasing the temperature can increase the chemical reaction rate, and lowering the temperature can decrease the chemical reaction rate.
3. Pressure
(1) The effect of pressure on the rate of chemical reaction is essentially achieved by changing the effect of concentration on the rate of chemical reaction.
(2) Since the volume of solid or liquid is very little affected by pressure, pressure only affects the reaction rate of chemical reactions involving gas.
(3) Changing the pressure must cause a change in the concentration of the reactants or products to change the chemical reaction rate. Otherwise, the chemical reaction rate remains unchanged.
Such as constant temperature and constant volume: filling with rare gas → the pressure of the container increases, the concentration of each reactant remains unchanged → the chemical reaction rate remains unchanged.
4. Catalyst
Catalysts can change the chemical reaction rates of forward and reverse reactions to the same extent.
5. Solid contact area
The chemical reaction rate is related to the size of the solid particles. The smaller the particles, the larger the surface area, and the faster the chemical reaction rate.
[Knowledge Expansion] Understanding the influence of pressure on reaction rate
Changing the pressure of a gas essentially changes the concentration of the gas substance, thereby achieving the purpose of changing (increasing or decreasing) the rate of chemical reaction.
Common situations include the following:
【Think·Discussion】
(1) Will increasing the amount of reactants definitely increase the rate of chemical reaction? Why?
Tip: Not necessarily, the concentration of solid and pure liquid reactants is a constant, increasing the amount of solid and pure liquid substances, the chemical reaction rate remains unchanged.
(2) As the temperature increases, do the rates of endothermic and exothermic reactions increase?
Tip: Speed up everything. As the temperature increases, molecular motion accelerates, the number of effective collisions per unit time increases, and the reaction rate inevitably accelerates.
(3) After changing the pressure, will the chemical reaction rate definitely change?
Tip: Not necessarily. The fundamental reason why changing the pressure affects the rate of chemical reaction is the change in concentration. When the pressure changes but has no effect on the concentration of the substance, the rate of the chemical reaction remains unchanged. For example, when "inert gas" is introduced into a closed container with constant volume, the rate of chemical reaction remains unchanged.
Keywords: Free download of PPT courseware for compulsory course 2 of high school chemistry in Lu Ke version, PPT download of the speed and limits of chemical reactions, PPT download of the rules of chemical bonding and chemical reactions, PPT download of the speed of chemical reactions, .PPT format;
For more information about the PPT courseware "Chemical Bonding Chemical Reaction Laws, Speed and Limits of Chemical Reactions, Chemical Reactions Speed", please click on the Chemical Bonding Chemical Reaction Laws, Speed and Limits of Chemical Reactions ppt, Chemical Reactions Speed and Limits ppt tag.
"The Speed and Limits of Chemical Reactions" Laws of Chemical Bonding and Chemical Reactions PPT (Lesson 2: The Limits of Chemical Reactions):
"The Speed and Limits of Chemical Reactions" Chemical Bonding Chemical Reaction Rules PPT (Lesson 2: Limits of Chemical Reactions) Part 1 Content: Foundation of Essential Knowledge Literacy 1. Reversible Reaction 1. Meaning: Under the same conditions, can _______ at the same time Reactions proceed in both directions. 2..
"Chemical Reactions and Energy Transformation" Chemical Bonding and Chemical Reaction Rules PPT (Lesson 2):
"Chemical Reactions and Energy Conversion" Chemical Bonding and Chemical Reaction Rules PPT (Lesson 2) Part One Content: Foundation of Essential Knowledge Literacy 1. Structure and Principle of Primary Battery 1. Primary Battery Principle (1) Primary Battery: A kind of utilization of ____________ _Will_________________..
"Chemical Reactions and Energy Transformation" Chemical Bonding and Chemical Reaction Laws PPT (Lesson 1):
"Chemical Reactions and Energy Transformation" PPT on the rules of chemical bonding and chemical reactions (Lesson 1) Part 1: Foundation for necessary knowledge literacy 1. Experimental exploration of energy changes in chemical changes 1. [Activity Exploration] 2. Conclusion: Every chemical reaction All accompanied by changes in energy...
File Info
Update Time: 2024-11-21
This template belongs to Chemistry courseware Lu Ke Edition High School Chemistry Compulsory Course 2 industry PPT template
"The Speed and Limits of Chemical Reactions" Chemical Bonding and Chemical Reaction Rules PPT (Lesson 1: The Speed of Chemical Reactions) Simple campus recruitment activity planning plan summary enterprise and institution recruitment publicity lecture PPT template is a general PPT template for business post competition provided by the manuscript PPT, simple campus recruitment activity planning plan summary enterprise and institution recruitment promotion Lecture PPT template, you can edit and modify the text and pictures in the source file by downloading the source file. If you want more exquisite business PPT templates, you can come to grid resource. Doug resource PPT, massive PPT template slide material download, we only make high-quality PPT templates!
Tips: If you open the template and feel that it is not suitable for all your needs, you can search for related content "The Speed and Limits of Chemical Reactions" Chemical Bonding and Chemical Reaction Rules PPT (Lesson 1: The Speed of Chemical Reactions) is enough.
How to use the Windows system template
Directly decompress the file and use it with office or wps
How to use the Mac system template
Directly decompress the file and use it Office or wps can be used
Related reading
For more detailed PPT-related tutorials and font tutorials, you can view: Click to see
How to create a high-quality technological sense PPT? 4 ways to share the bottom of the box
Notice
Do not download in WeChat, Zhihu, QQ, built-in browsers, please use mobile browsers to download! If you are a mobile phone user, please download it on your computer!
1. The manuscript PPT is only for study and reference, please delete it 24 hours after downloading.
2. If the resource involves your legitimate rights and interests, delete it immediately.
3. Contact information: service@daogebangong.com
"The Speed and Limits of Chemical Reactions" Chemical Bonding and Chemical Reaction Rules PPT (Lesson 1: The Speed of Chemical Reactions), due to usage restrictions, it is only for personal study and reference use. For commercial use, please go to the relevant official website for authorization.
(Personal non-commercial use refers to the use of this font to complete the display of personal works, including but not limited to the design of personal papers, resumes, etc.)
Preview