| Category | Format | Size |
|---|---|---|
| People's Education Press seventh grade biology book volume 2 | pptx | 6 MB |
Description
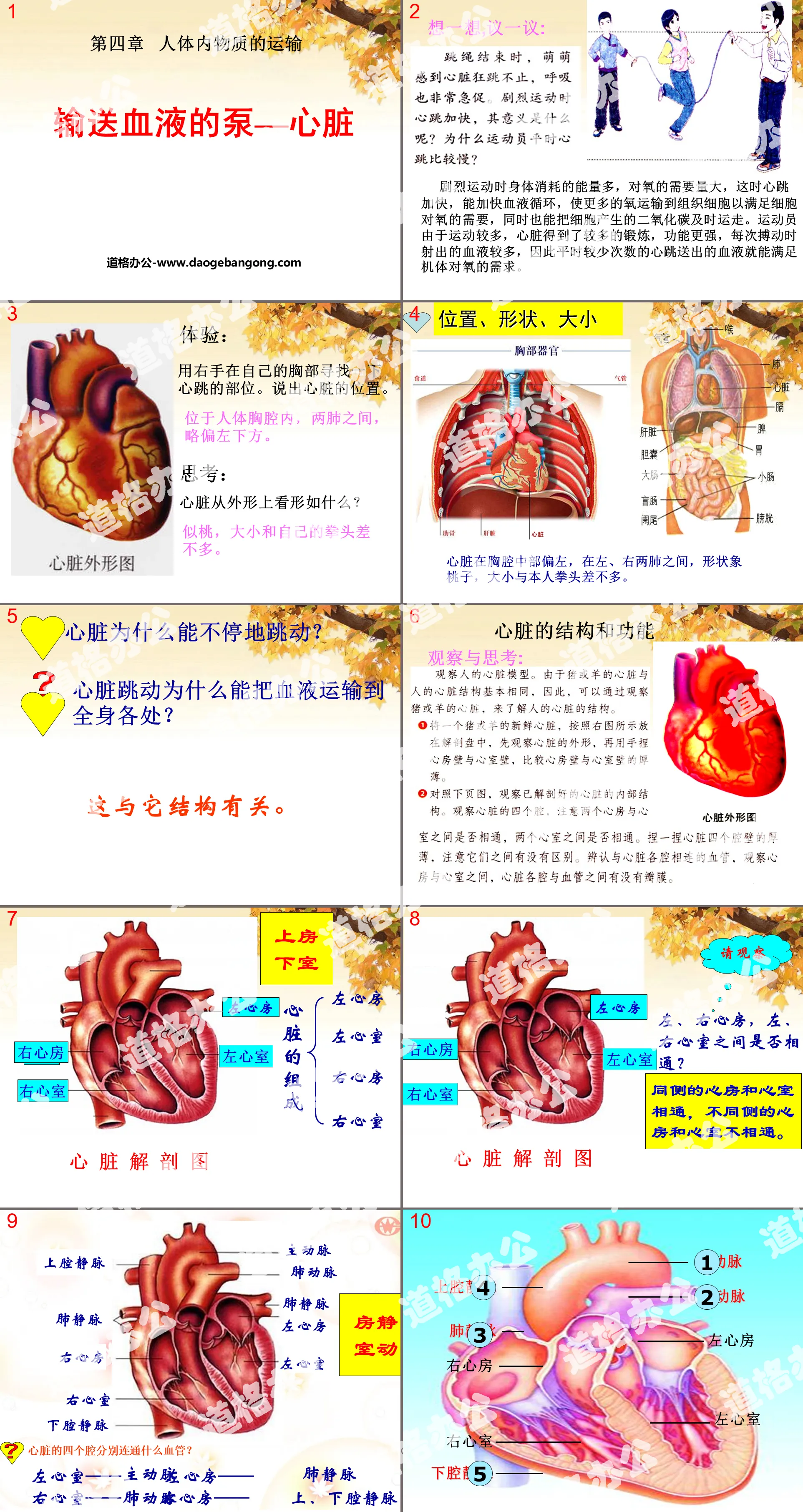
"The Pump that Transports Blood - Heart" Transport of Materials in the Human Body PPT Courseware 4
Think about it and discuss it:
During strenuous exercise, the body consumes a lot of energy and has a large demand for oxygen. At this time, the heartbeat speeds up, which can speed up blood circulation and transport more oxygen to tissue cells to meet the cells' oxygen needs. At the same time, it can also release the oxygen produced by the cells. The carbon dioxide is transported away in time. Because athletes exercise more, their hearts get more exercise, become stronger, and eject more blood with each beat. Therefore, the blood sent out by a smaller number of heartbeats can meet the body's demand for oxygen.
Experience:
Use your right hand to find the heartbeat on your chest. Name the position of the heart.
It is located in the human chest, between the two lungs, slightly to the lower left.
think:
What does the heart look like from the outside?
It looks like a peach, about the same size as my fist.
Observe and think:
1. What tissue is the heart wall mainly made of? What functions can be inferred from this?
Answer: The heart wall is mainly composed of muscle tissue. Muscle tissue has the functions of contraction and relaxation. Therefore, the heart can promote blood circulation in the blood vessels.
Why are the walls of the ventricles thicker than the walls of the atria?
Why are the walls of the left ventricle thicker than those of the right ventricle?
The thicker the heart wall and the more muscular it is, the more powerful it can contract and relax. The blood is transported farther. Compared with the atrium, the wall of the ventricle is thicker, because the blood in the atrium only flows to the ventricle connected with it; the wall of the left ventricle is thicker than that of the right ventricle. Only when the left ventricle contracts strongly can it deliver blood to the whole body, and the right ventricle can deliver blood to the whole body. Transports blood to the lungs where it is very close. Normally, the thickness of the right ventricular wall is only 1/3 of the left ventricular wall.
We often see people doing handstands. Can blood also flow upward to the toes when standing upside down?
The heart has well-developed muscles and can contract powerfully to push blood throughout the body, up to the brain and down to the fingers and toes; and the arterial valves and atrioventricular valves prevent blood from flowing back. So even if you do a handstand, blood can flow up to your toes.
I see
The heart is the power organ of blood circulation. It contracts and relaxes day and night to promote blood circulation in the blood vessels.
So how does blood circulate between the heart and blood vessels?
Systemic circulation: blood enters the aorta from the left ventricle, then passes through arteries, capillary networks, and veins at all levels throughout the body, and finally collects into the superior and inferior vena cava and flows back to the right atrium. This circulation path is called systemic circulation. In the systemic circulation, when blood flows through the capillary network around tissue cells in various parts of the body, it not only supplies the transported nutrients to the tissue cells for use, but also takes away waste products such as carbon dioxide produced by the cells. The hemoglobin in the red blood cells also removes the transported nutrients. The bound oxygen is released for use by cells. In this way, the blood changes from arterial blood that is rich in oxygen and bright red in color to venous blood that is less oxygenated and dark red in color.
Pulmonary circulation Blood enters the pulmonary artery from the right ventricle, passes through the capillary network of the lungs, and then flows back to the left atrium through the pulmonary veins. This circulation path is called pulmonary circulation. When blood flows through the capillary network of the lungs, carbon dioxide in the blood enters the alveoli, and oxygen in the alveoli enters the blood and combines with hemoglobin in red blood cells. In this way, the blood changes from venous blood with less oxygen and dark red color to arterial blood with rich oxygen content and bright red color.
It can be seen that the systemic circulation is the blood starting from the left side of the heart and returning to the right side, and the pulmonary circulation is the blood starting from the right side of the heart and returning to the left side, thus forming a complete blood circulation pathway.
1. Imagine that when a red blood cell starts from the left ventricle and returns to the heart through the blood circulation, what paths does it take? When it starts from the right ventricle of the heart again and returns to the heart through blood circulation, what paths does it go through?
Answer: When red blood cells start from the left ventricle and return to the heart through blood circulation, the path they go through is: left ventricle → aorta → arterioles → capillaries → venules → superior or inferior vena cava → right atrium. Starting from the right ventricle and returning to the heart through blood circulation, the path it takes is: right ventricle → pulmonary artery → capillaries of the lungs → pulmonary veins → left atrium.
2. In the above two circulation paths, what changes occur in the composition of the blood? What's the point?
Answer: The process of blood starting from the left ventricle and returning to the heart through blood circulation is systemic circulation. This process can transport nutrients and oxygen to tissue cells, and at the same time transport away waste products such as carbon dioxide produced by tissue cells. Blood starts from the right ventricle and returns to the heart through blood circulation. This is the pulmonary circulation. Through this process, the carbon dioxide in the blood is transported to the lungs and then discharged through the lungs. At the same time, the abundant oxygen in the alveoli is transported to the heart.
Do the math
When a person is at rest, the amount of blood ejected from the ventricle each time is approximately 70 ml. The total volume of blood in the human body is approximately 4000 ml. If the heart rate is 75 beats/minute, calculate:
1. How long does it take for all the blood in your body to circulate?
2. How many times does it cycle in a day (24 hours)?
3. How much blood does your heart pump in total in a day?
4000/70×75=0.76(minutes)
24×60/0.76=1895(times)
70×75×60×24=7560(L)
Take your family’s blood pressure
Blood pressure refers to the lateral pressure of blood on the blood vessel wall and can be measured at the brachial artery in the upper arm with a sphygmomanometer.
When the heart contracts, the highest value the arterial blood pressure reaches is called systolic blood pressure; when the heart relaxes, the lowest value the arterial blood pressure reaches is called diastolic blood pressure. Doctors often express blood pressure in the form of "systolic/diastolic blood pressure." The systolic blood pressure of healthy adults is 12 to 18.6 kPa, and the diastolic blood pressure is 8 to 12 kPa. A blood pressure of 18.6/12 kPa or higher is high blood pressure, and a blood pressure lower than 12/6.7 kPa is hypotension. Both conditions are harmful to human health.
2. In the blood circulation, what path does venous blood take and how does it become arterial blood? How does arterial blood become venous blood?
Answer: In the pulmonary circulation, venous blood becomes arterial blood as it flows through the capillaries of the lungs.
In the systemic circulation, arterial blood becomes venous blood as it flows through capillaries throughout the body.
3. When people participate in labor or sports activities, the heartbeat will speed up, which can ensure that the blood output from the heart can meet the needs of the body. However, people who lack exercise will experience extremely fast heartbeats and may feel uncomfortable or even faint when performing strenuous exercise for a long time. why is that?
Answer: People who lack exercise have underdeveloped heart muscles, insufficient blood transfusion capabilities, and their heartbeats are too fast and uncomfortable, resulting in insufficient oxygen supply and fainting.
Keywords: Teaching courseware on the transportation of substances in the human body, teaching courseware on the pump heart that transports blood, Biology PPT courseware for the second volume of the seventh grade of the New People's Education Edition, download of the biology slide courseware for seventh grade, download PPT courseware on the transportation of substances in the human body, transporting blood Download the pump heart PPT courseware in .ppt format
For more information about the PPT courseware "Transportation of Substances in the Human Body and the Pump Heart that Transports Blood" PPT courseware, please click on the Transport of Substances in the Human Body PPT Pump Heart that Transports Blood PPT tag.
"The Pump that Transports Blood - Heart" Transport of Materials in the Human Body PPT Courseware 5:
"The Pump that Transports Blood - Heart" Transport of Materials in the Human Body PPT Courseware 5 1. The structure and function of the heart Observation and thinking: Observe the human heart model. Since the heart of a pig or sheep has basically the same structure as a human heart, you can observe the heart of a pig or sheep...
"The Pump that Transports Blood - Heart" Transport of Materials in the Human Body PPT Courseware 3:
"The Pump that Transports Blood - Heart" Transport of Materials in the Human Body PPT Courseware 3 Review 1. What are the components of blood? 2. What do RBC, WBC, Hb and PLT stand for? 3. What are the functions of plasma? The picture above is a human blood smear observed through a microscope,...
"The Pump that Transports Blood - Heart" Transport of Materials in the Human Body PPT Courseware 2:
"The Pump that Transports Blood - Heart" Transport of Materials in the Human Body PPT Courseware 2 Pre-class Quiz 1. The bulging veins on our skin are actually ( ) A. Arteries b. Veins C. Capillaries D. Nerve 2. It can be used as a microscope to identify capillary...
File Info
Update Time: 2024-07-07
This template belongs to biology courseware People's Education Press seventh grade biology book volume 2 industry PPT template
"The Pump that Transports Blood - Heart" Transport of Materials in the Human Body PPT Courseware 4 Simple campus recruitment activity planning plan summary enterprise and institution recruitment publicity lecture PPT template is a general PPT template for business post competition provided by the manuscript PPT, simple campus recruitment activity planning plan summary enterprise and institution recruitment promotion Lecture PPT template, you can edit and modify the text and pictures in the source file by downloading the source file. If you want more exquisite business PPT templates, you can come to grid resource. Doug resource PPT, massive PPT template slide material download, we only make high-quality PPT templates!
Tips: If you open the template and feel that it is not suitable for all your needs, you can search for related content "The Pump that Transports Blood - Heart" Transport of Materials in the Human Body PPT Courseware 4 is enough.
How to use the Windows system template
Directly decompress the file and use it with office or wps
How to use the Mac system template
Directly decompress the file and use it Office or wps can be used
Related reading
For more detailed PPT-related tutorials and font tutorials, you can view: Click to see
How to create a high-quality technological sense PPT? 4 ways to share the bottom of the box
Notice
Do not download in WeChat, Zhihu, QQ, built-in browsers, please use mobile browsers to download! If you are a mobile phone user, please download it on your computer!
1. The manuscript PPT is only for study and reference, please delete it 24 hours after downloading.
2. If the resource involves your legitimate rights and interests, delete it immediately.
3. Contact information: service@daogebangong.com
"The Pump that Transports Blood - Heart" Transport of Materials in the Human Body PPT Courseware 4, due to usage restrictions, it is only for personal study and reference use. For commercial use, please go to the relevant official website for authorization.
(Personal non-commercial use refers to the use of this font to complete the display of personal works, including but not limited to the design of personal papers, resumes, etc.)
Preview