We all know that the income statement is a statement that reflects the operating results of a company during a certain accounting period. So, in actual use, how do we understand the income statement of a certain company?
We can analyze it from two aspects: the content of the income statement and the structure of the income statement.

1. Contents of the income statement
The presentation of the income statement should fully reflect the main sources and components of the company's operating performance, help usersjudge the quality and risks of net profit, and help users >Forecast profit sustainability, Make correct decisions.
(1) Sources and composition of operating performance
The popular understanding is the revenue component of a company.
(2) Expenses during the accounting period
Refers to costs, taxes and surcharges, period expenses, non-operating expenses, etc.
(3) The income statement is generally filled in according to the "step-by-step method"
Mainly reflects the three indicators of the company's "operating profit", "total profit" and "net profit".
1. Operating profit = operating income - operating costs - taxes and surcharges - operating expenses - administrative expenses - financial expenses
Operating revenue:
Includes main business income and other business income
Main business income is the income generated by the company's main business scope. For example, if the company mainly sells products, then the income from selling products is the main business income. Income; however, if the company sells some raw materials during its operations, it is considered other business income.
Operating costs:
Includes main business costs and other business costs, which correspond to the above operating income and will not be described again.
Taxes and surcharges:
Refers to consumption tax, urban maintenance and construction tax, education surcharge, local education surcharge, real estate tax, urban land use tax, Vehicle and vessel tax, stamp duty, etc.
Operating expenses:
Also called sales expenses, that is, wages, transportation expenses, depreciation expenses, entertainment expenses, travel expenses, advertising expenses, business promotion expenses, Sales discounts, etc.
Administrative expenses:
Mainly refers to wages, welfare fees, union funds, labor insurance premiums, board of directors fees, consulting fees, litigation fees, and business expenses incurred by the enterprise's administrative department Entertainment expenses, office expenses, travel expenses, depreciation expenses, R&D expenses, etc.
If the enterprise has a special R&D institution or incurs special research and development expenses, the R&D expenses need to be listed separately.
Financial expenses:
Mainly refers to various expenses incurred by enterprises to raise funds required for production and operation, mainly including bank fees, interest expenses (minus interest income), Cash discounts, net foreign exchange losses (minus exchange gains), etc.
Operating expenses, administrative expenses, and financial expenses are collectively called period expenses.
2. Total profit = operating profit + non-operating income - non-operating expenses
Non-operating income
Refers to various gains that are not directly related to the daily business activities of the enterprise.
Mainly include government rewards or subsidy funds, gains from disposal of non-current assets, gains from debt restructuring, gains from refinancing, gains from donations, etc.
Non-operating expenses
Refers to various expenditures that are not directly related to the daily production and operation activities of the enterprise.
Mainly include non-monetary asset exchange losses, debt restructuring losses, public welfare donation expenditures, extraordinary losses, losses, etc.
3. Net profit = total profit - income tax expense
Income tax expense = total profit * income tax rate
From the step-by-step method, we can see that when evaluating corporate operating results, non-operating income and expenses are extraordinary items, and we mainly Evaluation is based on the company's operating income, operating costs, expenses, etc.
2. Income statement structure
According to the content, the income statement generally has two forms:
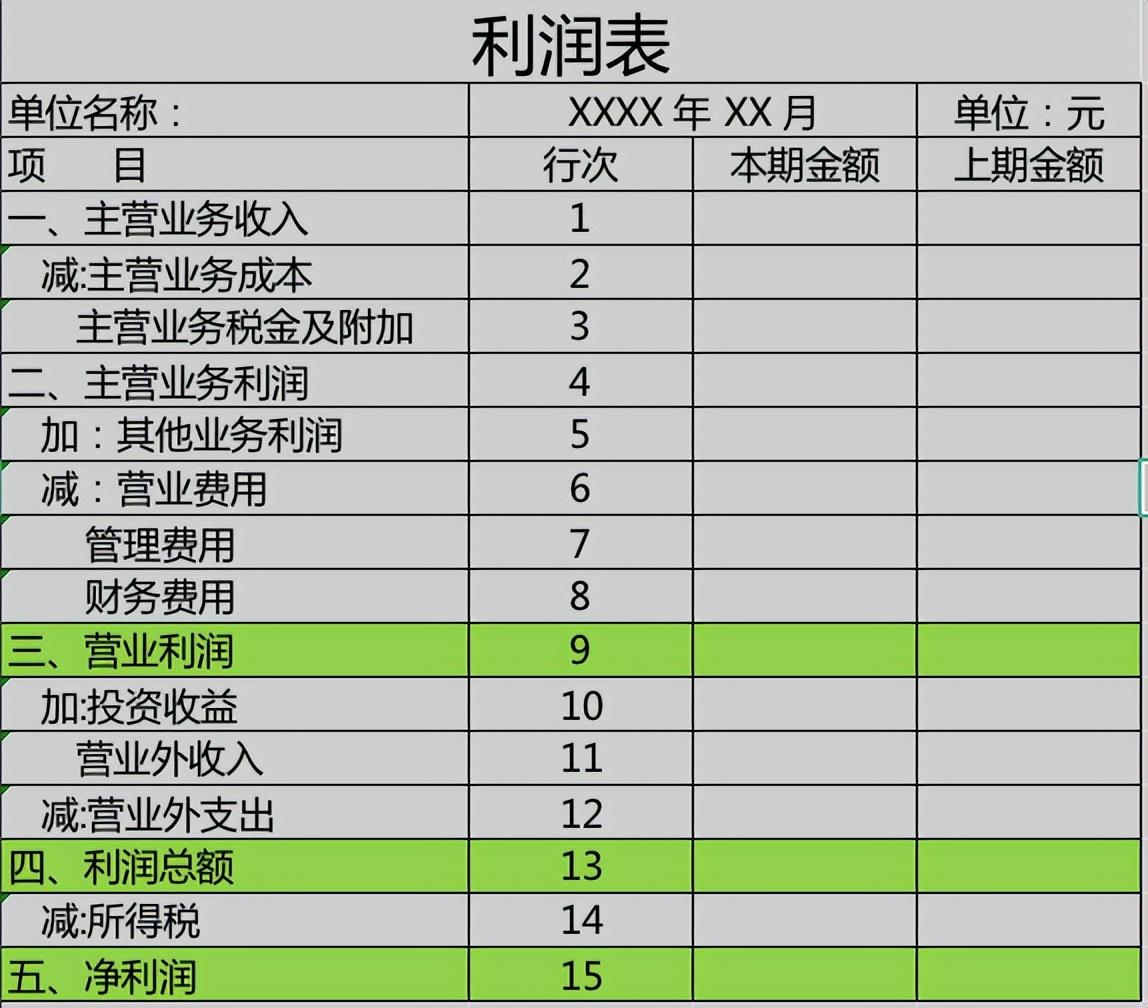
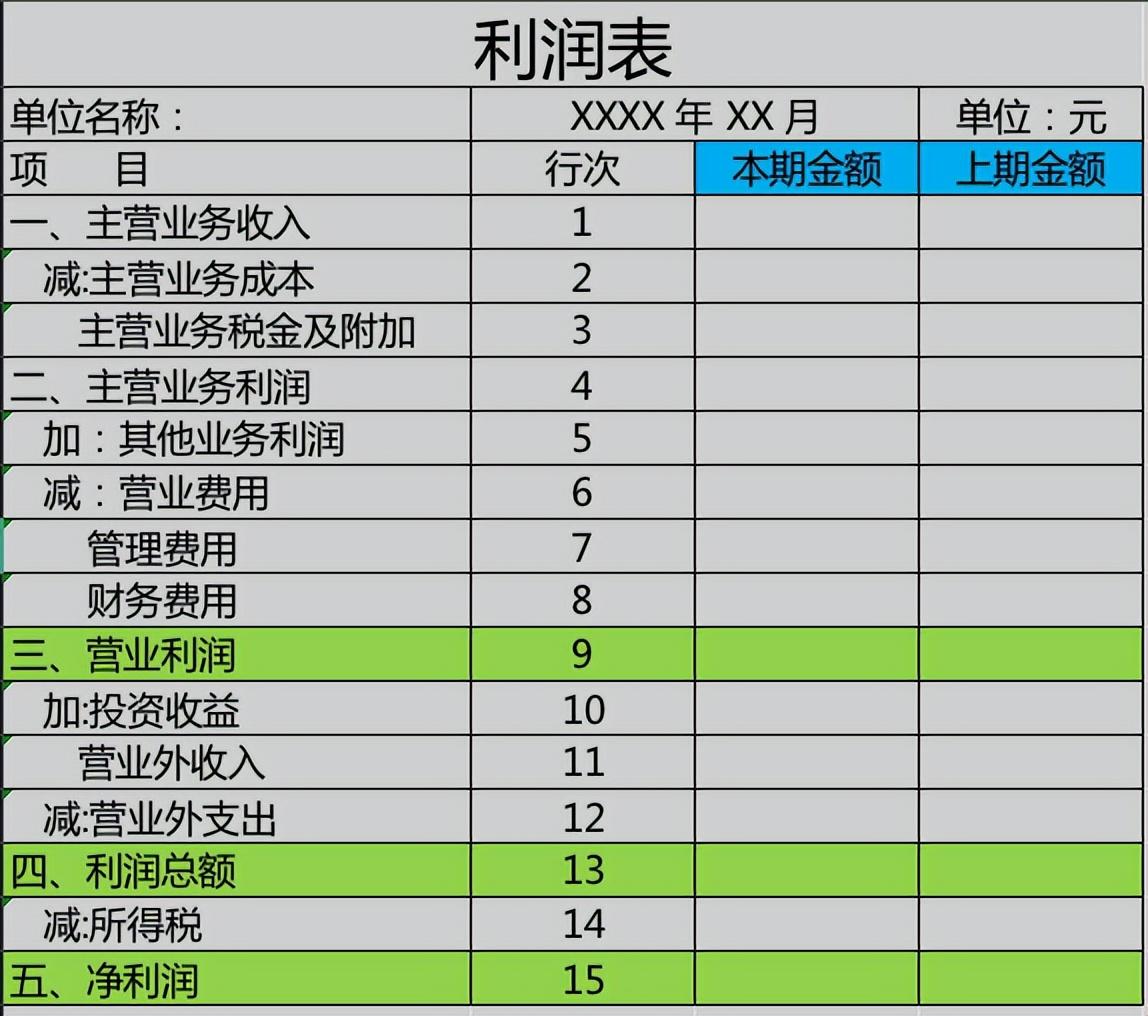
One is to reflect the current period data and the previous period data, which can conduct comparative analysis on the same period data and judge the same period or month-on-month data. ;
The other is to reflect the cumulative data of the current period and this year, which can make trend comparisons of the proportion of each expense, and then Determine whether the company's operating performance has improved or declined.
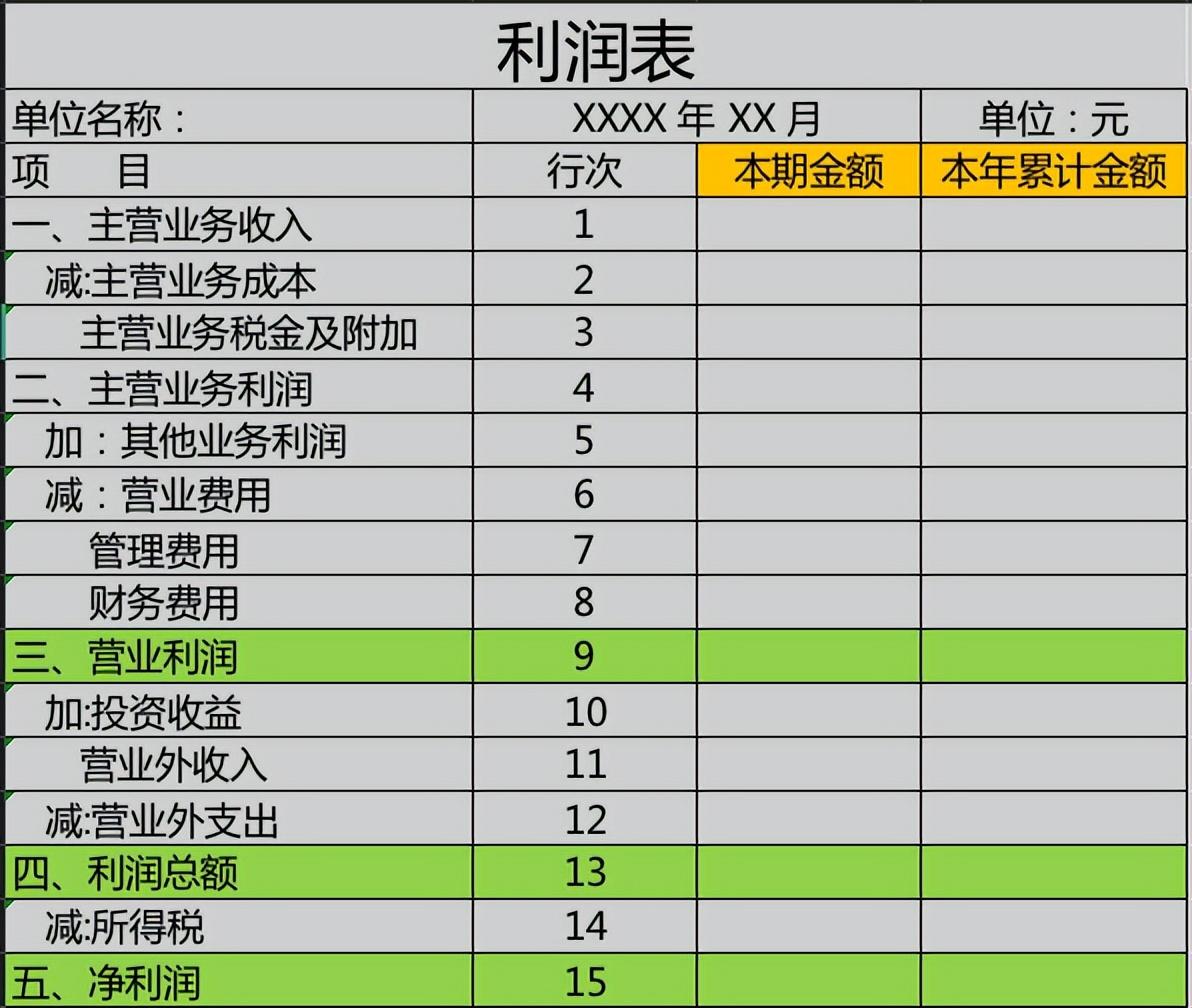
In specific analysis, data such as costs, tax surcharges, expenses, and non-operating income and expenses can be divided by income to calculate the proportion of each data , you can intuitively see the proportions of various data, and then judge the business performance of the company. At the same time, during specific analysis, it is also necessary to analyze the details of each expense in conjunction with the notes to the report. For example, if the proportion of operating expenses is high, it means that the company spends a large proportion of this item. You can analyze whether the publicity expenses or entertainment expenses are higher.
Financial analysis is a complex process, and each report user’s sensitivity and risk level to the proportion of various expenses are There are different preferences. How to understand the corporate income statement, the above is just a reference method, everyone can learn from each other, you are welcome to leave a message for discussion!
This article was originally written by "Silent Words 006". Welcome to pay attention and let us become a better version of ourselves together!
Articles are uploaded by users and are for non-commercial browsing only. Posted by: Lomu, please indicate the source: https://www.daogebangong.com/en/articles/detail/zen-me-kan-dong-qi-ye-de-li-run-biao.html

 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫 
评论列表(196条)
测试