Special explanation of mathematical probability for ninth grade students, classification analysis of four major test points + analysis of example questions + special exercises. Probability questions are one of the test points that will inevitably appear in the high school entrance examination. The problem of probability is no stranger to everyone in the learning process. During the learning process, the key is to focus on the definition of probability and the difference and connection between frequencies. Learn to use probability knowledge to explain practical problems in real life, master and break through this difficult point, and how to transform specific problems into abstract concepts.

The focus of learning is the classification of events, the definition of probability and the difference with frequency contact with. The difficulty lies in understanding the statistical regularity of random events.
1. Learning Objectives
1. Master the two methods of calculating probability, enumeration method and frequency estimation method;< /span>
2. Master the application of different methods for calculating probability.
2. Summary and sorting of knowledge points
1. Random events
(1) Determine the event
An event that can be sure to happen in advance It is called a necessary event. An event that can be determined in advance that it will definitely not happen is called an impossible event. Both necessary events and impossible events are certain.

(2) Random events
Under certain conditions, events that may or may not occur are called random events.
(3) Events are divided into certain events and uncertain events (random events), and certain events are divided into inevitable events and impossible events. Among them,
①The probability of an inevitable event occurring is 1, that is, P (inevitable event) = 1;
②The probability of an impossible event occurring is 0, that is, P (impossible event) = 0;
③If A is an uncertain event (random event), then 0
2. Possibility

(1) Theoretical calculation is divided into the following two situations:
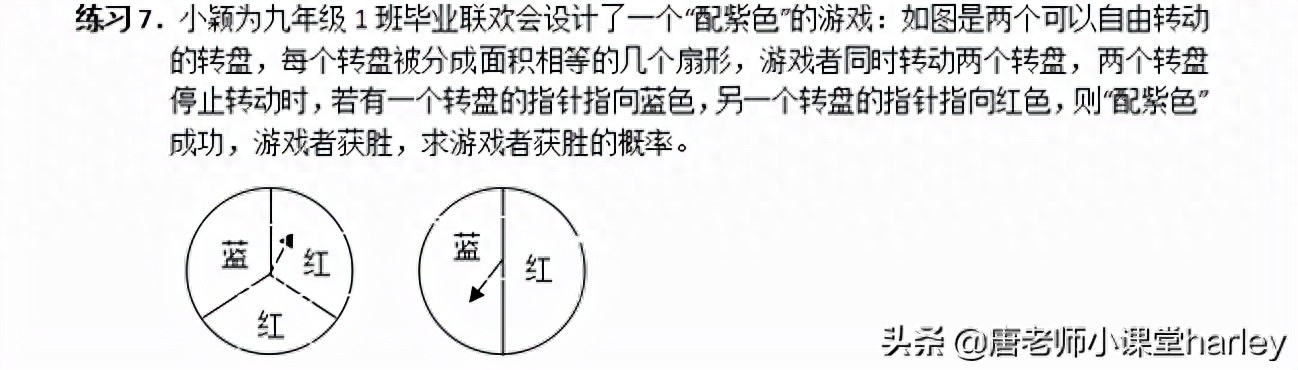
One: the probability of a random event involving only one step of experiment, such as: calculation of a type of probability model based on the relationship between probability and area; second: calculation through list method, enumeration method, and tree diagram The probability of random events involving two or more steps of experiment, such as matching purple, calculation of whether the game is fair.
(2) Experimental estimation is divided into the following two situations:
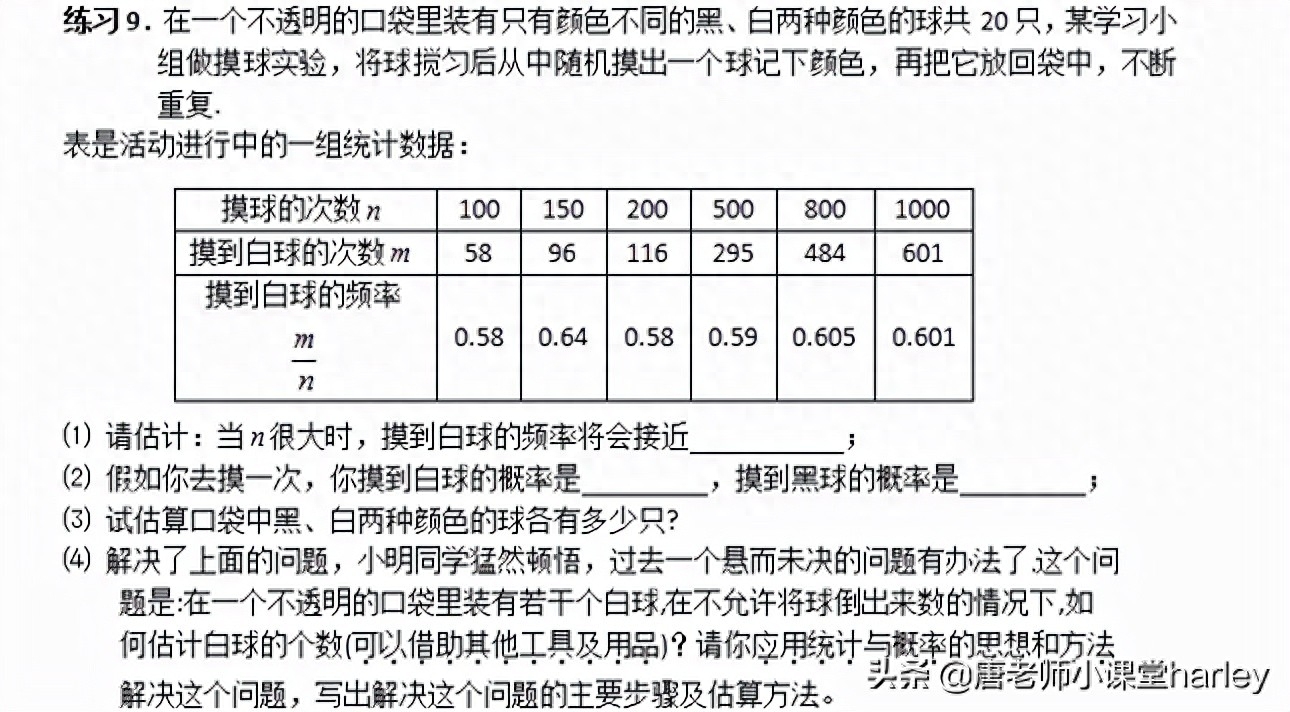
The first one: use experimental methods to estimate probability. It should be known that when the number of experiments is very large, the experimental frequency can be used as an estimate of the probability of an event occurring, that is, the frequency of a large number of experiments is stable at the theoretical probability.
Second type: Use simulation experiments to estimate probability. For example, use a calculator to generate random numbers to simulate experiments.
3. The meaning of probability
(1) Generally, in a large number of repeated experiments, if event A occurs The frequency mn will stabilize near a certain constant p, then this constant p is called the probability of event A, recorded as P(A)=p.

(2) Probability is the stable value of frequency (multiple) fluctuations, which is a measure of the likelihood of an event occurring. Performance.
(3) Probability range: _________.
(4) The probability of an inevitable event P(A)=1; the probability of an impossible event P(A)=0.
(4) The greater the likelihood of an event occurring, the closer the probability is to 1; the smaller the likelihood of an event occurring, the closer the probability is to 0.
(5) Make reasonable decisions in uncertain situations by designing a simple probability model; probability is closely related to real life. By understanding what is a fair game for both parties, use the language of probability to explain the fairness of the game. , and can design the probability model of the game as required, and combined with specific practical problems, understand the relationship between probability and statistics, and can solve some practical problems.
4. Method of finding probability
(1) Use _______ to find probability
(2) Use _________ probability
5. Game fairness
(1) To judge the fairness of the game, you need to first calculate the probability of each event, and then Compare the probabilities. If the probabilities are equal, it is fair. Otherwise, it is unfair.
(2) Probability = total number of situations required.

Three and four major test points + analysis of classic examples
1. Events and Probability
[Example 1] Which of the following events is inevitable ( )
A. Turn on the TV and the football game is being broadcast
B. The yield per mu of wheat must be 1,000 kilograms
C. Find 1 ball from the bag containing only 5 red balls , it’s a red ball
D. You can definitely see the full moon on the night of the 15th day of the lunar calendar
[Analysis] The definition of inevitable event is something that will definitely happen, you can choose Answer.

2. Use area to find probability
[Example 3] As shown in the figure, a sector is divided into 6 equal parts and can rotate freely. Turn the turntable. When the turntable stops, what is the probability that the pointer will point to the red area?

[Analysis] The circle is divided into 6 parts, 3 of which are red, that’s it Find the probability.


3. Find the probability by enumeration
[Example 4] There are two uniform turntables AB that can rotate freely, both of which are Divided into 3 equal parts, each part is marked with a number.
As shown in the picture. The rules are as follows:
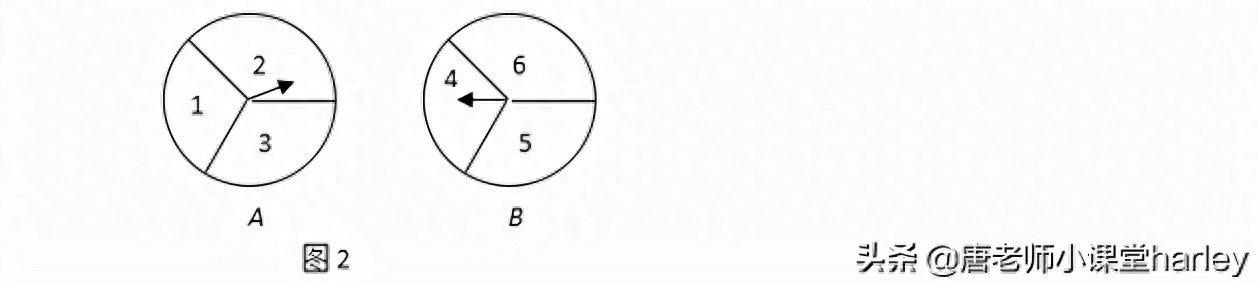
①Turn turntable A\B respectively;
②After the two turntables stop, point the two pointers Multiply the numbers (if the pointer stops on the bisector line, then reload until the pointer points to a certain part).
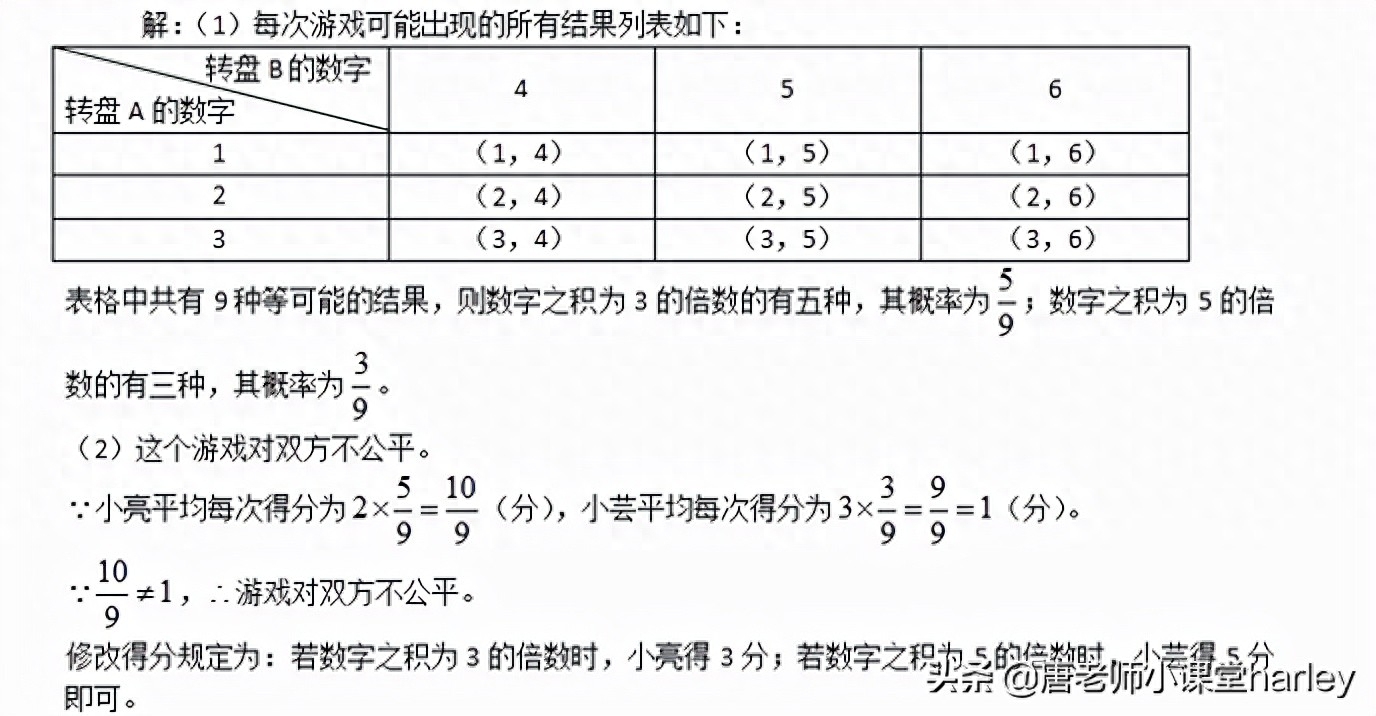
(1) Use the list method (or tree diagram) to find the number of numbers respectively The probability that the product of a product is a multiple of 3 and the product of a number is a multiple of 5;
(2) Xiaoliang and Xiaoyun want to use these two turntables to play games. They stipulated that when the product of the numbers is a multiple of 3, Xiao Liang gets 2 points; when the product of the numbers is a multiple of 5, Xiao Yun gets 3 points. Is this game fair to both parties? Please explain the reasons; if you think it is unfair, try to modify the scoring rules to make the game fair to both parties.

[Analysis] (1) The problem of finding the product of the numbers on two turntables, You can list all the situations and then find the probability of the corresponding conclusion. (2) Determine the probability of each situation separately, and then determine whether it is fair.
4. Frequency method to estimate probability
[Example 5] In order to test two coins, Xiao Ming engraved the number 1 on each of the six sides. , 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6. Are the regular hexahedral dice of good quality? Under the same conditions, throw two dice at the same time 20,000 times. It turns out that the sum of the two upward points is 7 20 times. . Do you think the quality of these two dice is acceptable (the standard of qualification is: when the dice are thrown under the same conditions, all sides of the dice have an equal chance of facing up)? and explain the reasons.

[Analysis] This question can be calculated separately by calculating the sum of the two upward points to be 7 The probability and experiment of 20,000 times appear two
Through the above explanation of the four major test points of probability and the analysis of example questions, students will have a better understanding of probability. The understanding of the question types is basically relatively comprehensive. During the learning process, students should pay more attention to understanding the concepts and regularities. This is the part that is more difficult for everyone or difficult to understand. For each test point, students must conduct detailed analysis and understand its test points. Only with regularity can you master the method of solving questions, so as not to lose this part of the score.
Articles are uploaded by users and are for non-commercial browsing only. Posted by: Lomu, please indicate the source: https://www.daogebangong.com/en/articles/detail/jiu-nian-ji-shu-xue-gai-lyu-zhuan-ti-jiang-jie-si-da-kao-dian-fen-lei-jie-xi-li-ti-jie-xi-zhuan-ti-lian-xi.html

 支付宝扫一扫
支付宝扫一扫 
评论列表(196条)
测试